Remote Lacunar Infarction
They are responsible for about 20 percent of all strokes. According to the National Institutes of Health NIH.

Lacunar Stroke An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Infarct of the brain.

Remote lacunar infarction
. Lacunar Infarct Right Remote Subacute Lacunar Infarct on Left Severe Cerebral Atherosclerosis. Lacunar infarcts are small 2 to 15 mm in diameter noncortical infarcts caused by occlusion of a single penetrating branch of a large cerebral artery 12. Here we used diffusion MRI and tractography to 1 spatially characterize microstructural abnormalities along WM tracts containing a lacunar infarct and 2 relate abnormalities in remote parts of the affected WM tract to cognitive outcome.These arteries are small and are uniquely vulnerable. Lacunar infarcts may cause disturbances of the white matter WM structure remote from the primary lesion. These branches arise at acute angles from the large arteries of the circle of Willis stem of the middle cerebral artery MCA or the basilar artery.
Lacunar infarcts are small infarcts in the distal distribution of deep penetrating vessels lenticulostriate thalamoperforating and pontine perforating arteries recurrent artery of Heubner. Lacunar infarcts small deep infarcts that result from occlusion of a penetrating artery account for about a quarter of all ischaemic strokes. Lacunar infarct is a small stroke - death of a small number of brain cells that is caused by closing of a small artery that is supplying them with oxy.
A lacunar stroke occurs when one of the arteries that provide blood to the brains deep structures is blocked. The most common lacunar syndrome is pure motor hemiparesis which accounts for 30-60 of lacunar infarcts. These infarcts have commonly been regarded as benign vascular lesions with a favourable long-term prognosis.
However recent studies have shown that this is only the case early in the disease course. Clinically lacunar strokes are recognized by characteristic clinical features. These arteries are quite small which makes them.
Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic stroke that occurs when blood flow to one of the small arteries deep within the brain becomes blocked. Less common causes of lacunar infarction include microemboli arterial dissection and arteritis secondary to chronic meningitis. Lacunar infarcts are small infarcts in the deeper parts of the brain basal ganglia thalamus white matter and in the brain stem.
They result from occlusion of one of the small penetrating end arteries at the base of the brain and are due to fibrinoid degeneration. Lacunar infarct is a type of stroke that occurs when one of the arteries supplying blood to the brain gets blocked. Lacunar strokes are a common occurrence in patients with vascular risk factors and can lead to a wide range of cognitive and sensorimotor sequelae.
Cognitive deficits following lacunar strokes may be more prevalent than sensorimotor symptoms and are characterized by impaired verbal fluency executive dysfunction and. Lacunar Infarct Key study points. Unlike most arteries which gradually taper to a smaller size the small arteries of a lacunar stroke branch directly off of a large high-pressure heavily muscled main artery.
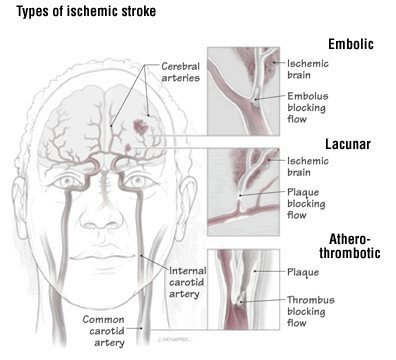
Lacunar Stroke Guide Causes Symptoms And Treatment Options
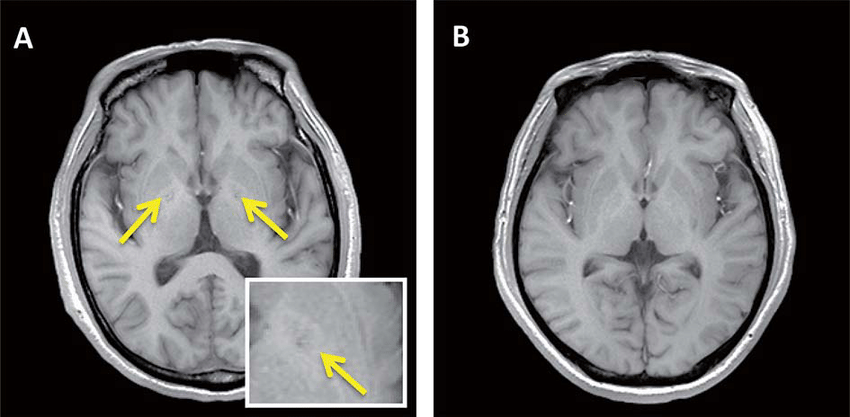
Example Of Silent Lacunar Infarcts On T1 Weighted Mri A A 65 Year Old Download Scientific Diagram

Lacunar Stroke Ischemic Stroke Stroke Cva Causes Disorders Braininjury Explanation Com

Example Of Silent Lacunar Infarcts On T1 Weighted Mri A A 65 Year Old Download Scientific Diagram

Lacunar Infarction Medlink Neurology



Posting Komentar untuk "Remote Lacunar Infarction"